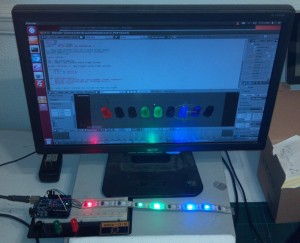
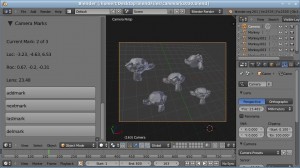
I guess I’ve been using Blender for so much for so long that I tend to look for ‘Blender-like’ controls in a/v projects. So inevitably when I started working with LED strips I immediately tried to weasel out of having to think through functions and loops in arduino code to create effects I could do intuitively in Blender.
So after a few bad UI attempts I thought – hey, wish I could just design a light sequence in Blender and run it with ALT-A. So that’s what I did.
On the arduino side it’s using the FastSPI and CmdMessenger libraries for LED and serial communications.
The Blender script just reads the diffuse color in r-g-b from each LED objects material and spits it out to the USB port. Getting the pyserial library hooked up in Blender wasn’t a breeze but the “sys.path.append” line should help anyone having the same issues I did.
Here’s the arduino code and Blender file
(Using Arduino Duemilanove 328 and LED strip with WS2801 chips)
EDIT:
Blendernation article (Thanks Bart!)
I forgot to mention I’m using Ubuntu so the sys.path.append thing wont work for windows, you’ll have to find the pyserial library solution elsewhere (there’s plenty of reference out there)
Also – the script runs on each frame change. Here’s how that works (WARNING: kinda hacky) http://funkboxing.com/wordpress/?p=236
QUESTION: For any API guru’s out there – currently this script opens and closes the serial port on each framechange. I know this is radically inefficient. Any ideas on how to keep the serial port open persistently but to close it when blender closes?